
任務
Balance a creative learning ecosystem driven by technology and traditional tools, cultivate future citizens with computational thinking, creativity, and perseverance, and enable every child to express, create, and collaborate confidently in the AI era.

視覺
Become a global leader in AI + education innovation platforms, reshape learning environments, and make technology a catalyst for children's unlimited potential, not a replacement for human intelligence.
學習目標:SCALE
基於人工智能時代的核心素養,我們定義了五個教育目標(SCALE):

科學素養
Use AI to support scientific inquiry, guide children to actively explore scientific principles through the "questioning - experimenting - verifying" cycle. This practice helps them construct early scientific thinking frameworks and enhances both scientific cognition and practical skills.

計算思維
Utilize robot programming tools to teach children how to decompose problems, design algorithms, and debug/optimize solutions, fostering the development of logical thinking frameworks.

人工智能素養整合
Embed AI-driven interactive dialogues into creative learning pathways, supported by AI-powered analysis of learning data. Through visualized explanations of natural language processing and visual recognition principles, children gain deeper AI understanding and cultivate digital core literacy.

學會學習/元認知
Combine AI-generated content (AIGC) with embodied creation (e.g., robot programming, maker activities) through task-driven challenges and reflective cycles. By iterating through "planning - execution - review" processes, learners master cross-disciplinary innovation methods while developing self-regulated learning abilities, transcending traditional educational boundaries.

工程與;設計思維
Prioritize empathy by designing simulated social scenarios (e.g., interactive smart pets). This guides children to establish foundational Engineering Design Process (EDP) frameworks while solving real-world problems, strengthening their understanding of human society and achieving dual cultivation of engineering innovation and humanistic values.
教學負責人

Child Agency-Driven "Learning Through Creating (LTC)" Model
Guided by project-based learning (PBL), children apply knowledge to solve real-world problems. This approach emphasizes children's agency in the learning process, encouraging hands-on exploration. Through PBL, they identify, analyze, and resolve challenges in practical contexts, achieving true knowledge internalization and application.
AI Is Understandable and Learnable
AI tools (e.g., smart drawing tools, voice assistants) provide heuristic guidance while preserving children's autonomy in decision-making. Children learn foundational AI principles through accessible methods and develop skills to collaborate with AI effectively.
Boundaryless Learning Through Interdisciplinary Integration
Break down disciplinary silos with integrated AI + programming + maker courses, nurturing children's creativity, real-world problem-solving skills, and perseverance.
Social-Emotional Learning
Learning is inherently social. Through collaborative projects (child-AI or peer teamwork), children deepen cognition via interaction. Communication, role division, and social engagement foster self-awareness, teamwork, knowledge internalization, emotional regulation, and meaning-making.

學習工具
人工智能輔導系統
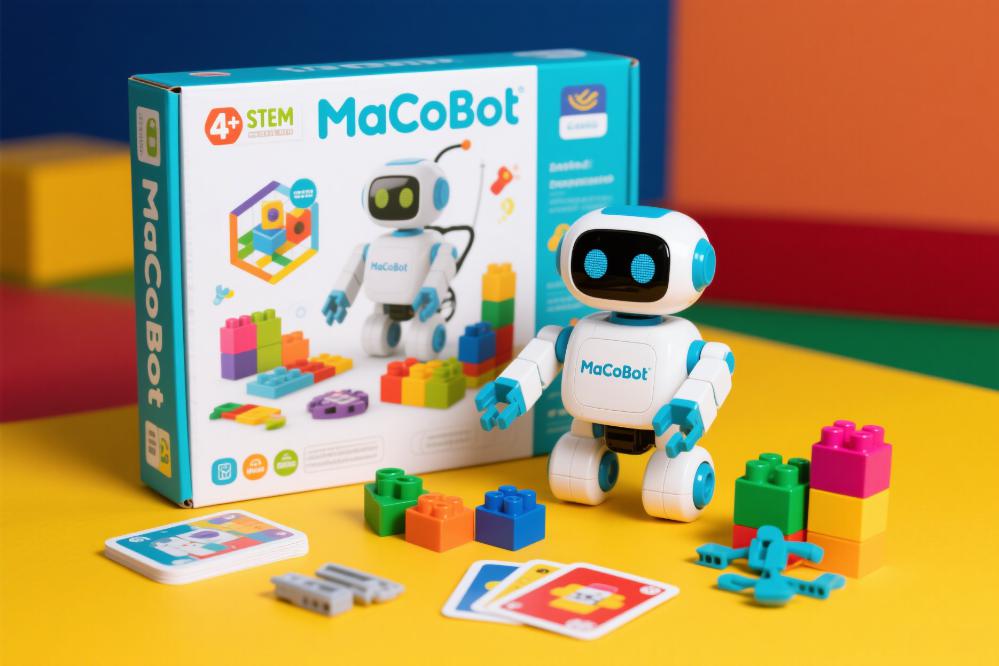

MaCoBot智能伴侶
- Voice-Activated Q&A Assistance
- Provide real-time learning progress updates to parents
- Simulate multi-sensory social-emotional interactions
編程機器人
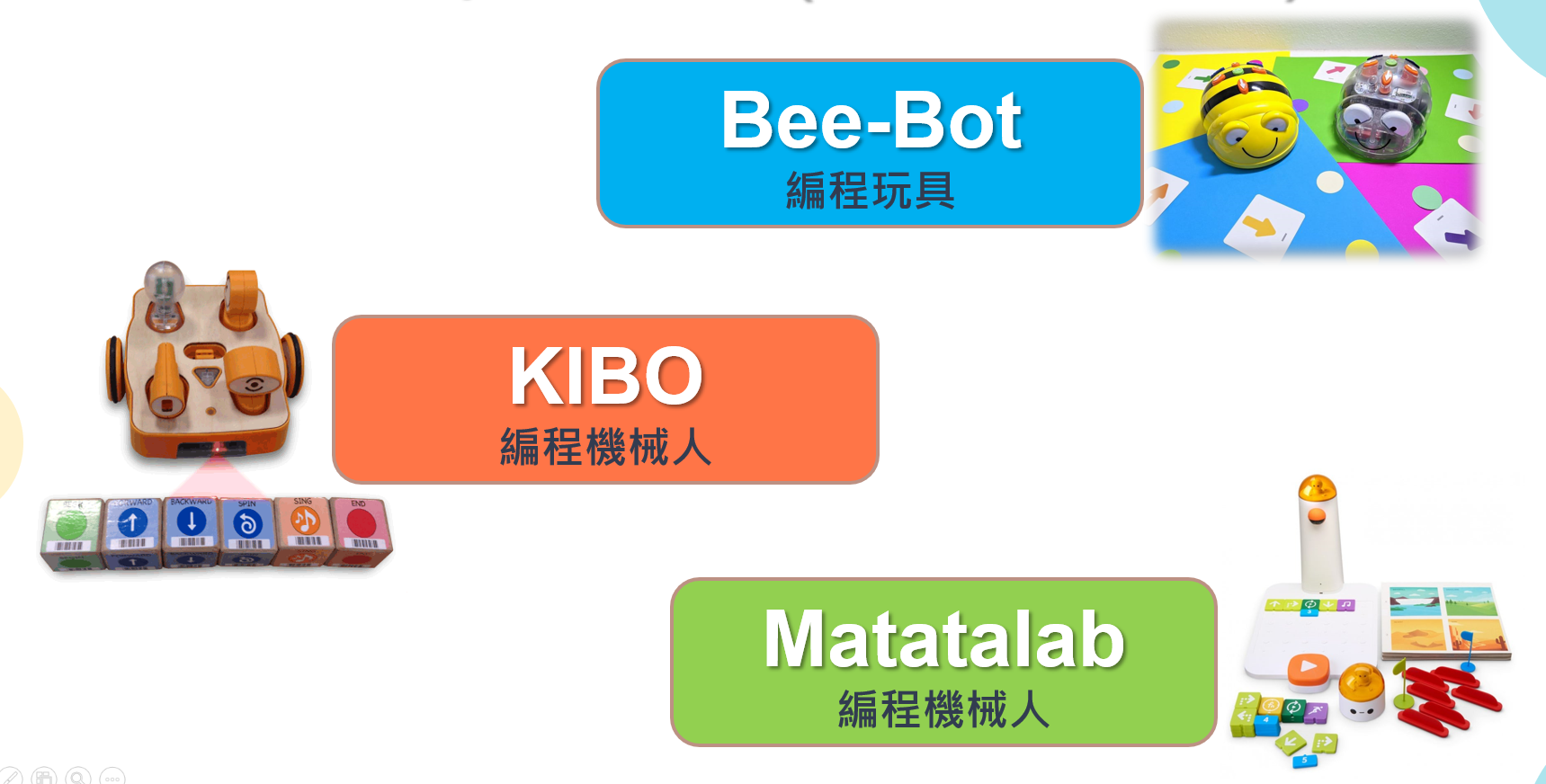
編程平臺
- No-Code Block Programming
- Control robots to complete tasks (e.g., maze navigation)
學習環境

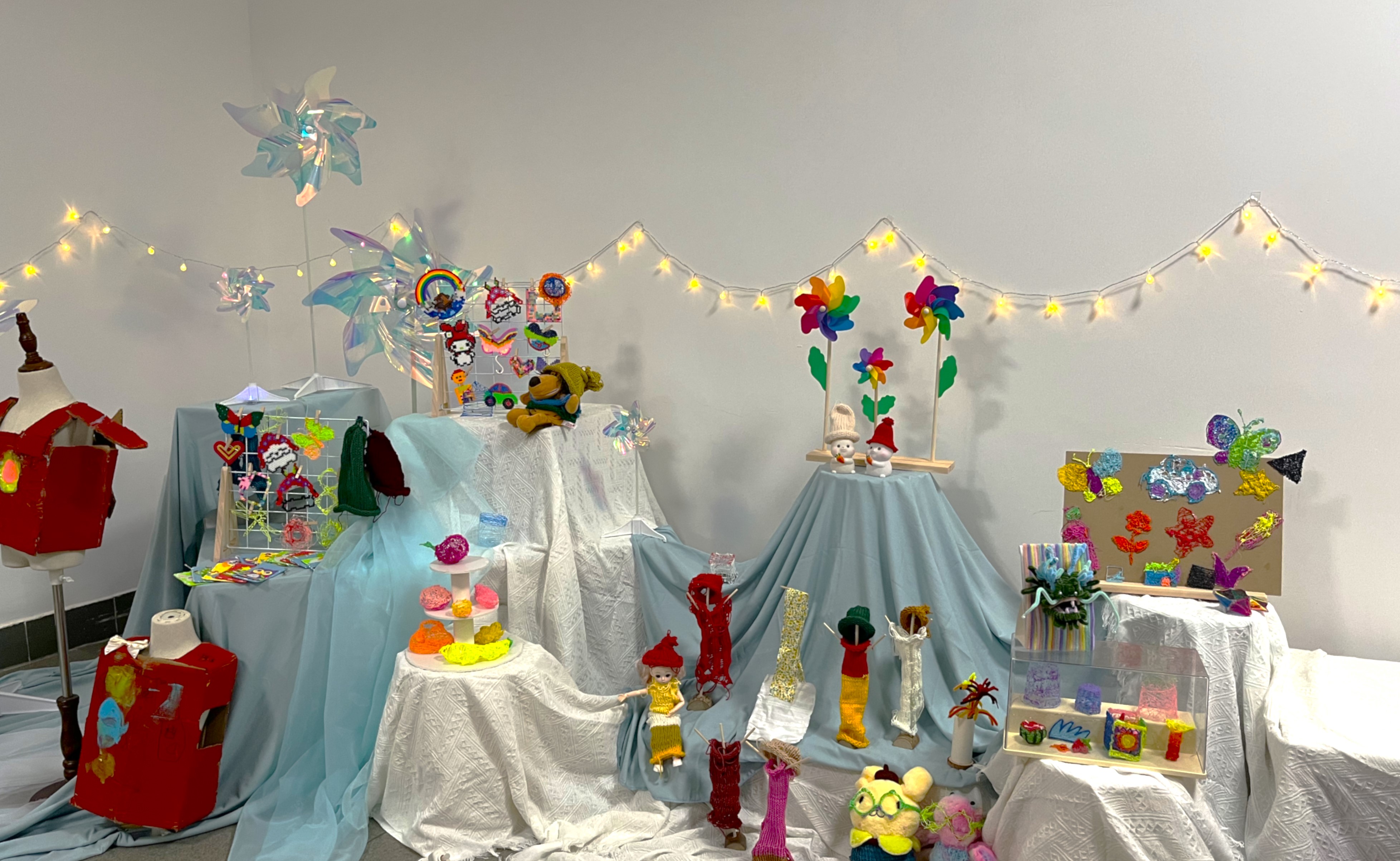
創客空間和材料套件
- Makerspace/Zone/Cart
- Child collaborative tasks (e.g., "Design a Future City")
教育者要求

創造性教學設計技巧
Use open-ended AI challenges in projects (e.g., "How can AI reduce food waste?") to guide children's self-directed exploration.

跨學科項目教學技巧
Integrate cross-disciplinary knowledge into teaching activities, enabling children to connect concepts across domains through vivid and engaging methods, helping them build effective learning capabilities.

倫理指導與;情感支持
Incorporate ethical discussions into the use of technological tools (such as "What if AI generates wrong answers?") to guide children to think dialectically about the role of technology and their relationship with it. Pay attention to children's emotional changes during learning to prevent technology dependence or frustration, and cultivate collaboration and communication skills, strengthening the awareness that "technology is a tool, and humans have more creativity.".
